Continuous Charge Distribution
Continuous Charge Distribution: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Continuous Charge Distribution, Line Charge Distribution, Surface Charge Distribution & Volume Charge Distribution etc.
Important Questions on Continuous Charge Distribution
A spherical conducting shell of inner radius and outer radius has a charge . A charge is placed at the centre of the shell.
What is the surface charge density on the (i) inner surface, (ii) outer surface of the shell?
Two isolated hollow spheres of radius and are charged to volts and volts respectively. Now the smaller sphere is inserted into the bigger sphere such that net charge on each sphere reamin same, then the potential difference between the two spheres becomes . Find .
Describe linear charge density. Write its SI unit.
What is volume charge distribution?
There is a conducting shell of inner radius and outer radius Inside this shell, there is a charge of at a distance of from the centre of the shell, then the force experienced by a charge at distance from the centre is
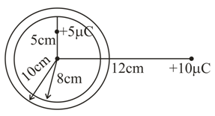
Two conducting spheres of radii and have equal surface charge densities. The ratio of their charges is ___.
Explain the term volume charge density. Write its SI unit.
Explain the term surface charge density. Write its Sl unit.
Find the total charge on a thin disc of radius , if its surface charge density varies with distance from centre as .
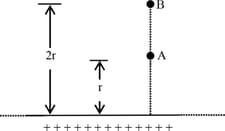
What will be the potential difference between two points and in front of an infinitely long line of charge of linear charge density , as shown in figure ?
A straight infinitely long cylinder of radius is uniformly charged with a surface charge density . The cylinder serves as a source of electrons, with the velocity of the emitted electrons perpendicular to its surface. Electron velocity must be to ensure that electrons can move away, from the axis of the cylinder to a distance greater than .
Two metal spheres, one of radius and the other of radius , both have same surface charge density . If they are brought in contact and separated, then the new surface charge density on each of the sphere are respectively
The surface density of charge on the surface of a charged conductor in the air is . Then the outward force per unit area of the charged conductor is
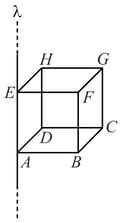
An infinite long line charge of charge per unit length is passing one of the edge of a cube. Length of edge of the cube is . (see figure)
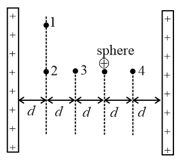
The figure shows two large, closely placed, parallel, nonconducting sheets with identical (positive) uniform surface charge densities, and a sphere with a uniform (positive) volume charge density. Four points marked as 1, 2, 3 and 4 are shown in the space in between. If are magnitude of net electric fields at these points respectively then:
A solid sphere of radius and volume charge density is enclosed by a hollow sphere of radius with negative surface charge density , such that the total charge in the system is zero, is a positive constant and r is the distance from the centre of the sphere. The ratio is
When a charge of amount is given to an isolated metal plate of surface area , its surface charge density becomes . When an isolated identical plate is brought closer to , the surface charge density on becomes . When is earthed, the surface charge density becomes . Then -
Two mutually perpendicular infinitely long lines of charge having charge per unit length as and are located in air at a distance from each other. The force of interaction between them is
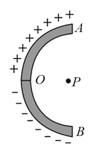
A thin glass rod is bent into a semicircle of radius . A charge is uniformly distributed along the upper half and a charge is uniformly distributed along the lower half, as show in diagram. The electric field at , the centre of the semicircle, is
A solid sphere of radius and volume charge density is enclosed by a hollow sphere of radius with negative surface charge density , such that the total charge in the system is zero, is a positive constant and is the distance from the centre of sphere. The ratio is
